Everyone who has ever seen a fire will know its ability to change and, usually, damage the things that it comes into contact with. And yet, not all these changes are the same. There are some chemical changes that can take place in response to high temperatures. So, what causes one substance to melt in flames but another to burn?
Melting is a “phase change” when a substance changes from a solid to a liquid but does not change its chemical formula. Burning, on the other hand, requires the combination of the substance, usually with oxygen, to form new compounds and chemicals.
This sounds confusing, but I will get into more detail to clear up the difference below. Let’s take a look at how this works and why it matters.
Your # 1 priority is keeping your family safe. As a firefighter, I recommend everyone has updated smoke detectors that don’t require battery changes, like these ones from Kidde, a fire extinguisher, like this one from Amerex, and a fire escape ladder if you have bedrooms above the first floor, I recommend this one from Hausse.
Also read: What Is The Temperature Of Fire? How Hot Does it Get?
What Is Melting?

Melting is a “phase change” as we’ve already said.
Most people have heard of the traditional states of matter:
- Solid
- Liquid
- Gas
These are also known as the traditional phases of matter.
In addition to these three phases, there are also four more that tend to only be known to physicists and chemists:
- Ionized plasma
- Quark-gluon plasma
- Bose-Einstein condensate
- Fermionic Condensate
These four phases of matter only occur under very specific conditions, and you don’t need to spend much time worrying about them in conjunction with fire.
Melting is a phase change between a substance being solid and then becoming liquid.
And boiling is the phase change that sees a substance change from liquid to gas.
It’s important to realize that this is not a chemical reaction as the substance is not changed into another substance by melting or boiling.
Why Does Something Melt?
In order to form a solid, the molecules within a substance need to bond to each other, these bonds can be strong bonds as they are in, say, diamond or sodium chloride (table salt) or relatively weak as they are in, say ice (frozen water) or Gallium (the metal).
In order to melt, the bonds between the molecules must be weakened or broken and allow the molecules to flow freely over each other (as liquids do).
To break these bonds, you will need to heat the substance.
Ice melts when heated by a drink or the room temperature around it.
The water molecules are freed up easily to return to their natural liquid state.
The same is true for Gallium, which will melt on a hot day (it has a melting temperature of about 30 degrees Celsius or 86 degrees Fahrenheit) with no extra effort required.
On the other hand, if you’re waiting for a diamond to melt by itself, you will be waiting a long time as you need to raise the temperature to about 7,280 degrees Fahrenheit (4,027 Celsius) to get the bonds in the diamond to break down to produce liquid carbon.
Table salt, Sodium Chloride, also requires a high temperature of 1,474 degrees Fahrenheit to melt (that’s 801 degrees Celsius).
Can Everything Be Melted?
Not every substance can be melted.
In fact, there are two things that might stop a substance from melting, even if you have an unlimited amount of heat:
- The substance doesn’t melt, it sublimates, instead. Sublimation is what happens when the bonds in the solid substance are broken down but instead of forming a liquid, the bonds are so weak that the substance becomes a gas, instead. Iodine is a wonderful example of a substance with no liquid phase. If you heat it, the solid breaks down into a purple gas. This can happen, slowly, even at room temperature!
- The substance doesn’t melt, it burns, instead. There are many substances that don’t melt under ordinary circumstances in a flame and that’s because they themselves catch fire before they can melt.
What Is Burning?
Burning is a chemical reaction.
That means the starting product is combined with oxygen (usually, it is, in fact, possible to “burn” substances in a variety of gasses but oxygen is the only one commonly available in the air) and creates a new compound.
These compounds may be solids, liquids, or gases, but no melting occurs because the starting material has been transformed into a different material.
The burning reaction is an “exothermic” reaction.
That means as the original material is consumed in the reaction, it releases heat and light.
This often means that “burning” is a self-sustaining reaction, as the heat required to continue the reaction is generated by the material being burned.
This is why fires will, normally, only self-extinguish when they run out of material to burn and why fire services and fire control equipment are essential in modern life to extinguish fires.
Also read: Is Fire Flammable? Can It Make More Fire?
Can Anything Be Burned?
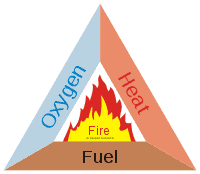
In order for something to burn there are some conditions that need to be met:
- You need a supply of fuel which must be able to react with oxygen
- You need a supply of oxygen (nothing burns without oxygen or another oxidizer, such as Chlorine, present to drive the chemical reaction)
- You need enough heat to start the reaction
In theory, this means that as long as you have a substance that reacts with oxygen and an unlimited amount of heat and oxygen, you can burn almost anything.
However, there are substances that don’t react with oxygen.
For example, Carbon Dioxide, in this instance carbon can be burned but it has already been burned in oxygen to form carbon dioxide.
Carbon dioxide is unable to further react with oxygen no matter how hot things get and thus, you cannot burn carbon dioxide.
Oxides are a good example of substances that can’t burn (and, indeed, this is why water does not burn it’s an oxide of hydrogen).
Now, it is possible to heat an oxide to a temperature so high that all the bonds between individual atoms are broken.
Thus, carbon dioxide becomes carbon and oxygen again.
If you were to reduce the heat, the carbon would catch fire in the oxygen and produce carbon dioxide again, but this does not mean you can burn carbon dioxide, it means you can burn carbon.
Also read: Does Fire Have Mass? What Does It Weigh?
Burning vs. Melting – Examples:
To better understand these differences between melting and burning, it might help to look at some examples and see what happens in them.
Why Does Wood Burn and Not Melt?
Wood is made out of many different materials.
It is not a single substance but rather a combination of water, cellulose, lignin, and a mixture of other chemicals in much smaller quantities.
When you heat the wood, the first thing that happens is the water evaporates off.
Water is a liquid, so it cannot melt, but at around 212 degrees Fahrenheit (100 degrees Celsius) it does boil and turn into a gas.
It’s important for the water vapor to leave the wood as while it contains water, the water will extinguish any fires.
Once the water is gone, what’s left is essentially “long-chain hydrocarbons” that are compounds made from carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
Breaking down these long-chain hydrocarbons for them to melt is a fairly complex process and it would require very high temperatures.
However, you won’t reach these temperatures because the hydrocarbons (which are similar to the chemicals found in petroleum) burn very easily and before melting would be possible, they react with the oxygen in the air.
This produces mainly water, carbon dioxide, and carbon monoxide and because of the temperatures involved, these will be produced as gasses.
Melting vs. Burning of Wax in a Candle?
Candle wax is a funny substance because it can melt AND it can burn in a flame.
So, what’s the difference?
Well, if you were to place your wax in a vacuum (no oxygen) and heat it, it would melt, but without any oxygen present, it would not burn.
The wax would change from solid to liquid and then, if you removed the heat for a while, it would return to solid-state (by freezing) without any loss of wax.
Your candle would weigh the same at the start of this process as at the end of it.
However, once oxygen is present, the wax will both melt AND burn.
The wax that burns is also a hydrocarbon and thus, produces mainly water, carbon dioxide, and carbon monoxide.
Once you remove the flame from a candle in oxygen, the melted part of the candle solidifies but the burned part does not and is lost.
Thus, a candle that is lit in the presence of oxygen will weigh less after being used than it did before being used as some wax is consumed by being burned.
Also read: Why Is My Candle Flame So High/Tall/Big/Small? Answered
Related Articles
What Makes Something Flammable?
Symbolism of Fire: Spiritual, Dreams, History
Is Oxygen (O2) Flammable? Actually No…
Is Smoke Flammable? You May Be Surprised…

